

Many time zones have more than one offset due to daylight saving time (aka "summer time") rules. Time Zone != OffsetĪ time zone can not be represented solely by an offset from UTC. However, many countries have changed their standard offset since then, such as when North Korea shifted from UTC+9 to UTC+8:30 in 2015.Ī related concept is Daylight saving time or Summer Time, which is an advance of (usually) one hour, mandated by many countries between spring and autumn. Nepal was the last country to adopt a standard offset, shifting slightly to UTC+5:45 in 1986. It took many decades before all time on Earth was in the form of time zones referred to some "standard offset" from GMT/UTC. Many applied the time at a local astronomical observatory to an entire country, without any reference to GMT. By about 1900, almost all time on Earth was in the form of standard time zones, only some of which used a hourly offset from GMT. Sandford Fleming of Canada proposed worldwide hourly time zones in 1879. The first time zone was created in 1847 by railroads on the island of Great Britain using GMT. When well-regulated mechanical clocks became widespread in the early 19th century, each city began to use some local mean solar time.

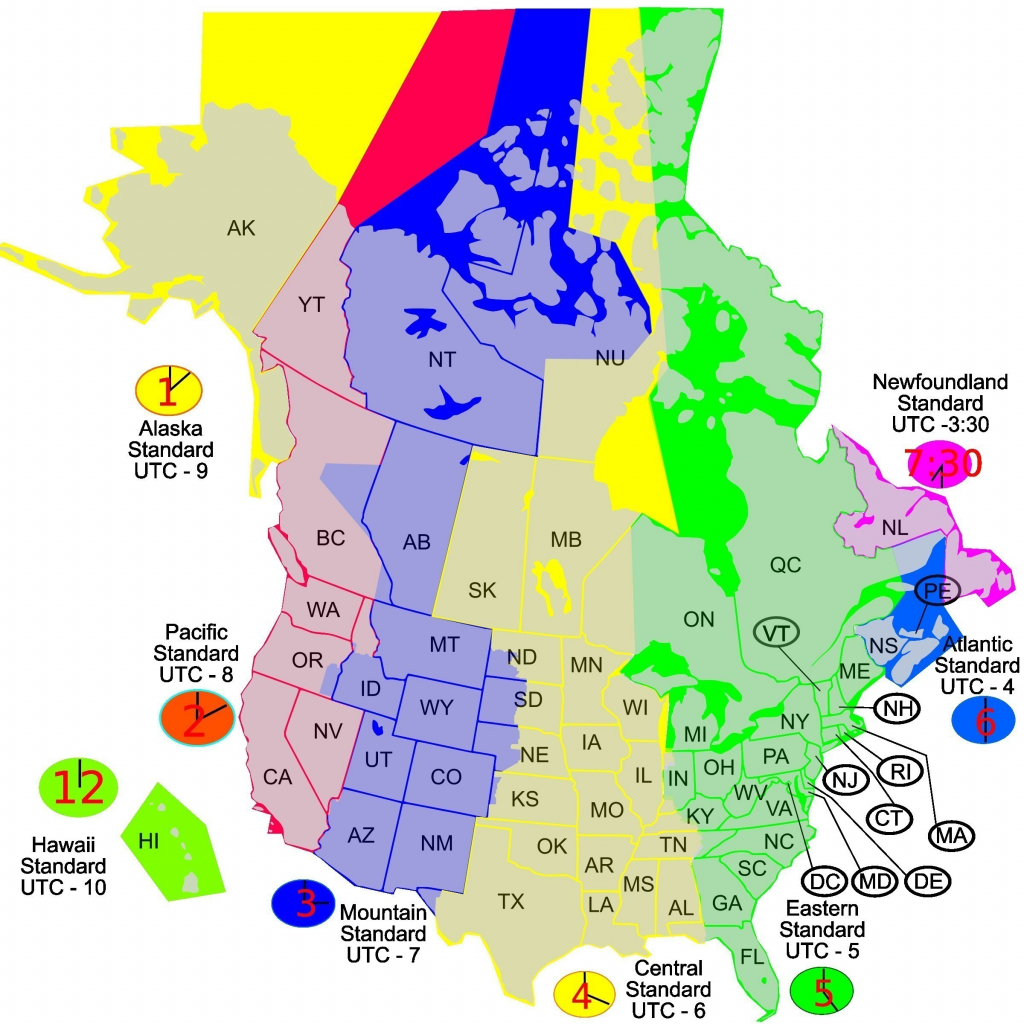
Originally, all time on Earth was some local apparent solar time, the time on a sundial, so every city had its own time. UTC, also called Zulu time, is used everywhere on Earth by astronomers and others who need to state the time of an event unambiguously. Many countries now legally define their standard time relative to UTC, although some still legally refer to GMT, including the United Kingdom itself. Since 1972, all official time services have broadcast radio time signals synchronized to UTC, a form of atomic time that includes leap seconds to keep it within 0.9 seconds of this former GMT, now called UT1. Many land time zones are skewed toward the west relative to the corresponding nautical time zones.īefore 1972, all time zones were specified as an offset from Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), which was the mean solar time at the meridian passing through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London, United Kingdom. Most (UTC−11 to UTC+11) are 15° of longitude wide, which is one hour of Earth's rotation relative to the Sun, but an hourly zone in the central Pacific Ocean is split into two 7.5° wide zones (UTC☑2) by the 180th meridian, part of which coincides with the International Date Line. In addition to land time zones, there are 25 nautical time zones, all separated by lines of longitude. Of the time zones on land, most have a standard-time offset from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) by a whole number of hours (UTC−12 to UTC+14), but several are offset by 30 or 45 minutes from a nearby hourly offset. General Information About Time ZonesĪlmost all time zones on land have legally defined borders which coincide with the borders of the country mandating the time or some subdivision thereof. As legal definitions of zones can vary wildly and change often, a database or lookup table is often required to properly apply time zone rules. Please read the entire tag wiki for details.Ī time zone is a region on Earth that has a uniform, legally mandated standard time. Do not mistake an offset such as -07:00 as a time zone. It is often represented by an identifier, such as "America/Los_Angeles". A time zone is a region on Earth that has a uniform, legally mandated standard time.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
